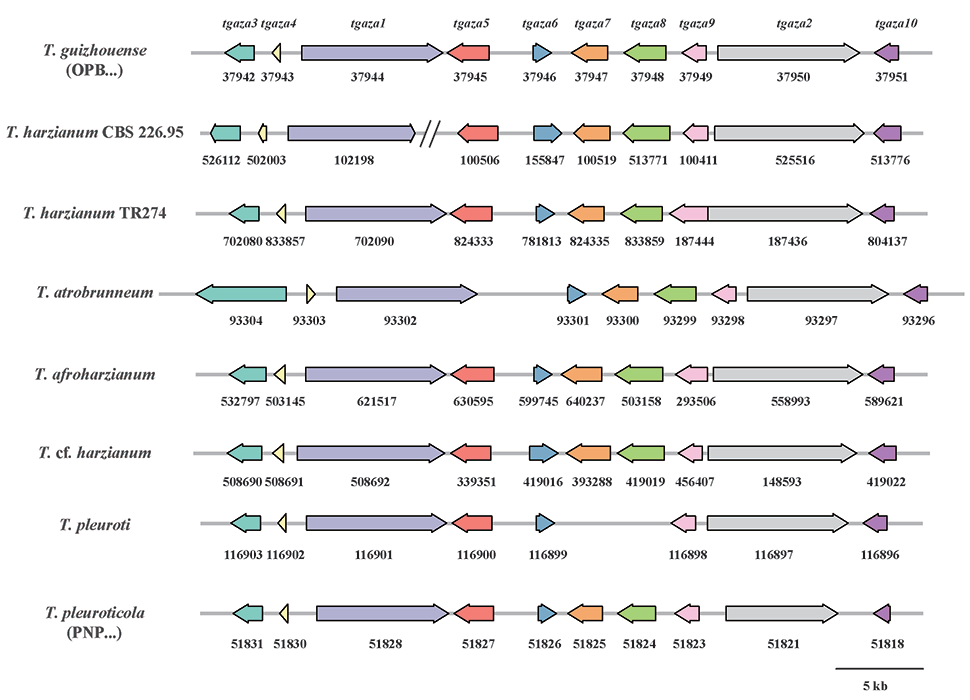
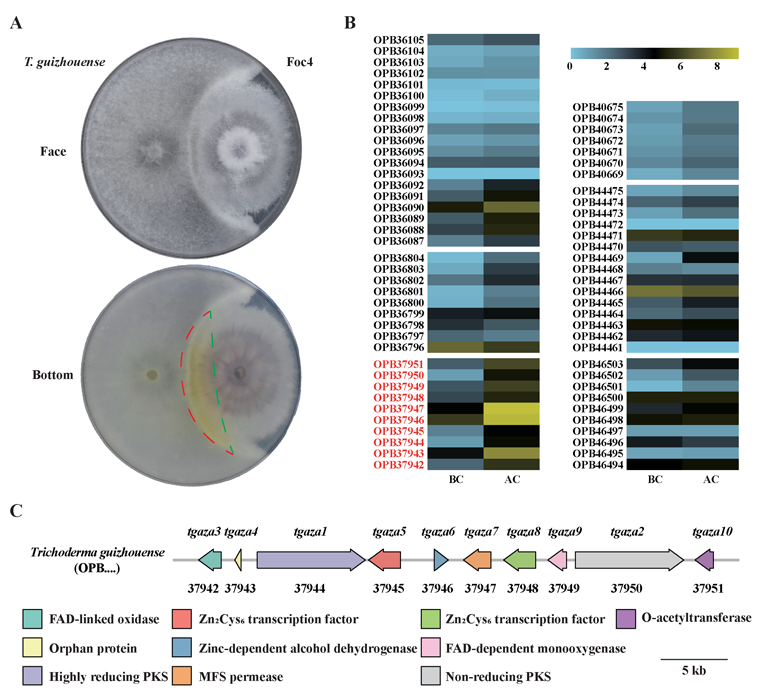
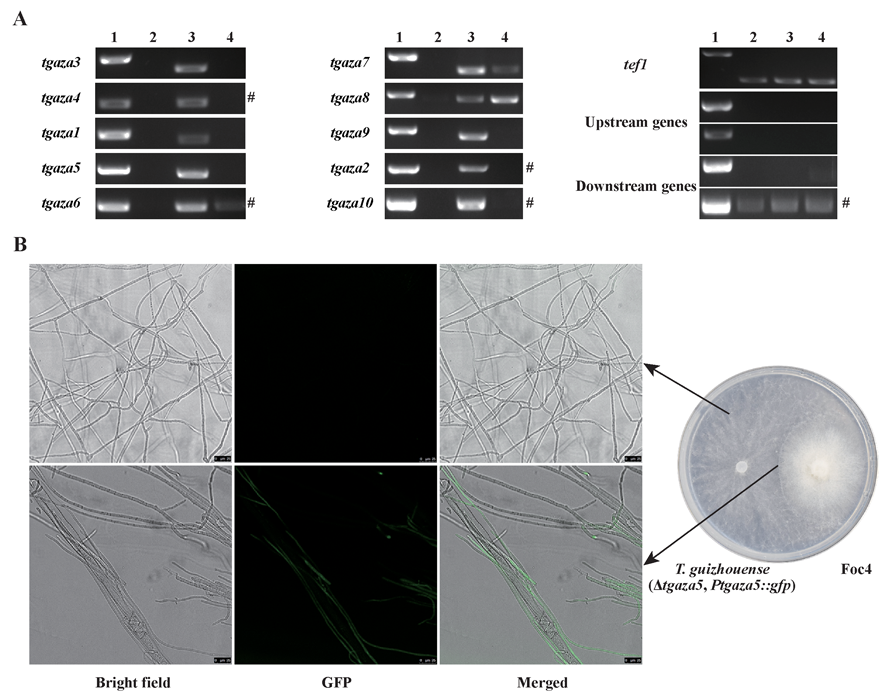
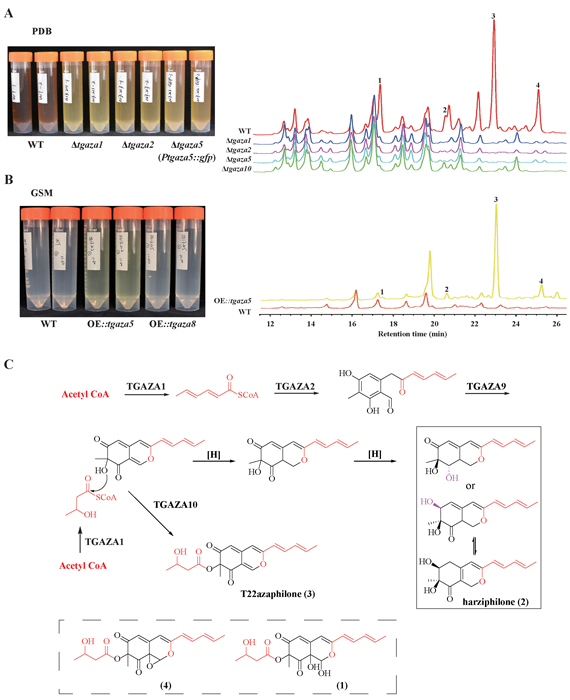
Siqiao Chen, a FungiG Ph.D. guest student researching the fungal-like bioeffectors used to control plant disease caused by Pythium spp. pathogen.
We studied the diversity of Trichoderma (Hypocreales, Ascomycota) – Pythium (Peronosporales, Oomycota) antagonistic interactions on a taxonomically-wide scale for a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing microbial dialogues in environmentally friendly control to Pythium diseases by next next-generation bioeffectors. For this purpose, we set a library of Trichoderma strains that represent the major taxonomic clades, and investigated their interactions with five species of causative plant diseases Pythium, and revealed that the ability to suppress Pythium is a generic property of Trichoderma as most species showed profound antagonism regardless of the partner identity. Furthermore, the soil-dwelling species, such as T. asperellum, T. atroviride and T. virens showed to be the most efficient. In contrast, canopy-associated and putatively strictly mycoparasitic species (T. minutisporum, T. parepimyces, and T. strictipile) were only moderately antagonistic to Pythium spp. These results suggest that the interactions with Pythium spp. benefit from the shared (core-genome) genetic traits of Trichoderma, such as hydrolytic enzymes that can degrade cellulose, one of the main polysaccharides of the water mold cell wall. Therefore, we harnessed exo-proteomics in combative interactions by liquid culture with Pythium mycelia to analyze the contribution of exo-emzymes (e.g. cellulases and proteases) to the antagonism. We also exploited the mutant of the highly cellulolytic species T. reesei lacking XYR1, which is the major transcriptional activator of cellulase gene expression to investigate the contribution of cellulases to the antagonism. The T. reesei △xyr1 mutant showed reduced antagonism levels to all of the five Pythium plant pathogens species analyzed compared to the wild-type. Still, the ability of Trichoderma to inhibit Pythium spp. was not abolished, suggesting other factors contributed to the antagonism. Our goal is to figure out the potential of Trichoderma bioeffectors to control diseases caused by Pythium plant pathogens, and molecular mechanisms of the multi-faceted nature of the antagonism.
CURRICULUM VITAE
Siqiao Chan,B.Sc.(Ag.)
Professional address: Nanjing Agricultural University, Weigang 1th, Nanjing, 210095, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
E-mail: 33315220@njau.edu.cn
Born on: Aug/15/1996, Huizhou, Guangdong, China
Web links: www.FungiG.org & ResearchGate
Education and trainings:
Sept/2019 ꟷPresent Directly Ph.D. study, College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, Nanjing Agricultural University, and Plant Protection Institute, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanjing, China. Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Qirong Shen Advisory board: Prof. Dr. Irina S. Druzhinina, Dr. Paul Daly.
Dec/2018 ꟷMar/2019 Undergraduate graduation thesis. Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Irina S. Druzhinina and Dr. Feng Cai
Jul/2018 ꟷAug/2018 Academic Summer camp, Boston, USA
Sept/2015 ꟷJul/2019 B.S. in Agro-grassland science, College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China
Research interests and skills:
Keywords: Fungal-like bioeffectors to Pythium plant diseases, fungal cellulases, exo-proteomics, fungal wars, Trichoderma genetic engineering.
Microbiological techniques: Axenic cultures, microbial diagnostics by DNA barcoding, fungal morphology, microbial cultivations, light, confocal, and scanning electron microscopy techniques.
Molecular biological techniques: Qualitative and quantitative nucleic acid manipulation techniques, protoplast transformation of Trichoderma and Pythium.
Proteomic and analytical techniques: Fungal exo-proteomics and basic proteomic assays, metaproteomic analysis
Fungal ecophysiology: BIOLOG phenotype microarrays, qualitative assays for enzymatic activity, dual confrontations of fungi, growth profiling.
Microbial metagenomics: Transcriptomics sequencing for fungi and Oomycota, absolute quantification technique, qPCR
Molecular evolution: Phylogenetics analyses, DNA barcoding of fungi and Oomycota
Other skills: Plant physiology, plant biochemical assays and nutrition
Publications:
- Daly, P., Chen, S., Xue, T., Li, J., Sheikh, T. M. M., Zhang, Q., Wang, X., Zhang, J., Fitzpatrick, D A., McGowan, J., Shi, X., Deng, S., Jiu, M., Zhou, D., Druzhinina, S I., Wei, L. (2021). Dual-Transcriptomic, Microscopic, and Biocontrol Analyses of the Interaction Between the Bioeffector Pythium oligandrum and the Pythium Soft-Rot of Ginger Pathogen Pythium myriotylum. Frontiers in microbiology, 12, 765872-765872.
- Xue, T., Wang L., Chen, S., Xie, W., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., Zhou, D., Wei, L. (2021). Analysis of the Pathogenicity of Ginger-infecting Pythium myriotylum Isolates Towards Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, submitted.
- Chen, S., Daly, P., Zhou, D., Li, J., Wang, X., Deng, S., Feng, H., Wang, C., Sheikh, T. M. M., Chen, Y., Xue, T., Cai, F., Kubicek, C P., Wei, L., Druzhinina S I. (2021). The use of mutant and engineered microbial agents for biological control of plant diseases caused by Pythium: achievements versus challenges, Fungal Biology Reviews, under review.